Using genetics to tackle the illegal ivory trade in Cambodia
18/05/2018 in Conservation
RZSS WildGenes are working with Fauna and Flora International (FFI) on a project to develop a conservation genetics laboratory in Cambodia’s capital, Phnom Penh. The Royal University of Phnom Penh (RUPP) was founded in 1960 and is the first Cambodian University to offer a Master’s degree in Conservation, thanks largely to support from FFI. Over the last few years, we have been working with scientific staff at RUPP on a project to study the few remaining wild elephants in Cambodia. Up to this point we have been extracting DNA from faecal samples to allow researchers to identify individuals using their genetic profile.

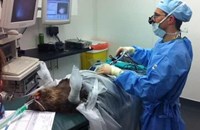
Above: Ivory samples need to be drilled to get the DNA encased within the tusk.
In a continuation of this collaboration with FFI and RUPP, we are now expanding our focus to include the ivory trade that is decimating elephant populations worldwide. Thanks to support from the players of People’s Postcode Lottery and a grant obtained from the DEFRA Illegal Wildlife Trade (IWT) Challenge Fund, we plan to use genetics to better understand the ivory trade within Cambodia. Within each ivory sample there are cells containing DNA that were encased as the tusk was growing. We can use this DNA to reveal important information about the individual elephant that grew the tusk, such as whether it was male or female and, crucially, where its closest relatives live. This second question is especially important as there seems to be very little evidence of poaching in the small fragmented populations left in Cambodia, yet there are large amounts of Ivory for sale within the domestic market. Understanding where the ivory is coming from is vital information for enforcement agencies looking to block illegal trade routes into the country. Further, if we can use genetics to identify where elephants are being killed for their ivory, measures can be taken to protect the remaining elephants most at risk of persecution.

Above: The ivory drilling process in the Cambodian laboratory.
Below: Some examples of ivory and hippo tooth.

The collaboration with RUPP also provides RZSS with an opportunity to build conservation knowledge and capacity within a country that has some of the few remaining wild landscapes in South East Asia. The Eastern Plains Landscape in North East Cambodia has the largest intact block of forest left in SE Asia, home to many endangered mammal species, including Asian elephants. The largest lake in SE Asia is also situated in Cambodia, the Tonle Sap, being home to the critically endangered Siamese crocodile and Mekong Giant catfish. By helping support and train staff at the first Conservation genetics laboratory in Cambodia, we hope to impart knowledge and resources for them to support future much needed conservation initiatives within their country.

Above: Asian elephant in the Eastern Plains Landscape, Cambodia.
I look forward to updating you again soon!
Alex
RZSS WildGenes work in Cambodia is proudly supported by DEFRA and the players of People's Postcode Lottery.
 |
 |
Featured Articles

An update from the Budongo Forest
19/04/2024 in Conservation

Edinburgh Zoo named best zoo in Scotland
15/04/2024 in Edinburgh Zoo
Latest News
-
Blog

20/01/2024
Penguin Awareness Day 2024
Edinburgh Zoo is home to the largest outdoor penguin pool in Europe, with three different species and over 100 individuals. This penguin awareness day get to know some of the famous faces in the colony who you can also watch live on our penguin cam.
-
Blog

21/09/2023
Tracking penguins in the Southern Oceans
Earlier this month at the 11th International Penguin Congress in Viña del Mar, Chile, Dr Heather Ritchie-Parker, one of our conservation charity’s research scientists, presented important data which explores the connectivity between endangered Northern rockhopper penguin colonies.
-
Blog

30/08/2023
A library for genetics
In a hidden area within the Royal Zoological Society of Scotland’s (RZSS) Edinburgh Zoo, the RZSS WildGenes Biobank preserves important genetic material for conservation research and population management.
-
Blog

24/07/2023
What’s on the menu for the European wildcats
European wildcat is a secretive species, and so it is difficult to observe their hunting and feeding behaviour in the wild. Analysing their scats is an alternative way to find out what they eat and therefore how they fit into the ecosystem. RZSS WildGenes scientists developed a technique to detect DNA of different prey species in scat samples.
























Follow EZ